Radio Climate Monitor
This document will guide you through the Radio Climate Monitor project. You will be able to see dashboard with temperature, humidity, ambient light and atmospheric pressure in Node-RED and view the data on your smart phone using the Blynk cloud and mobile app.
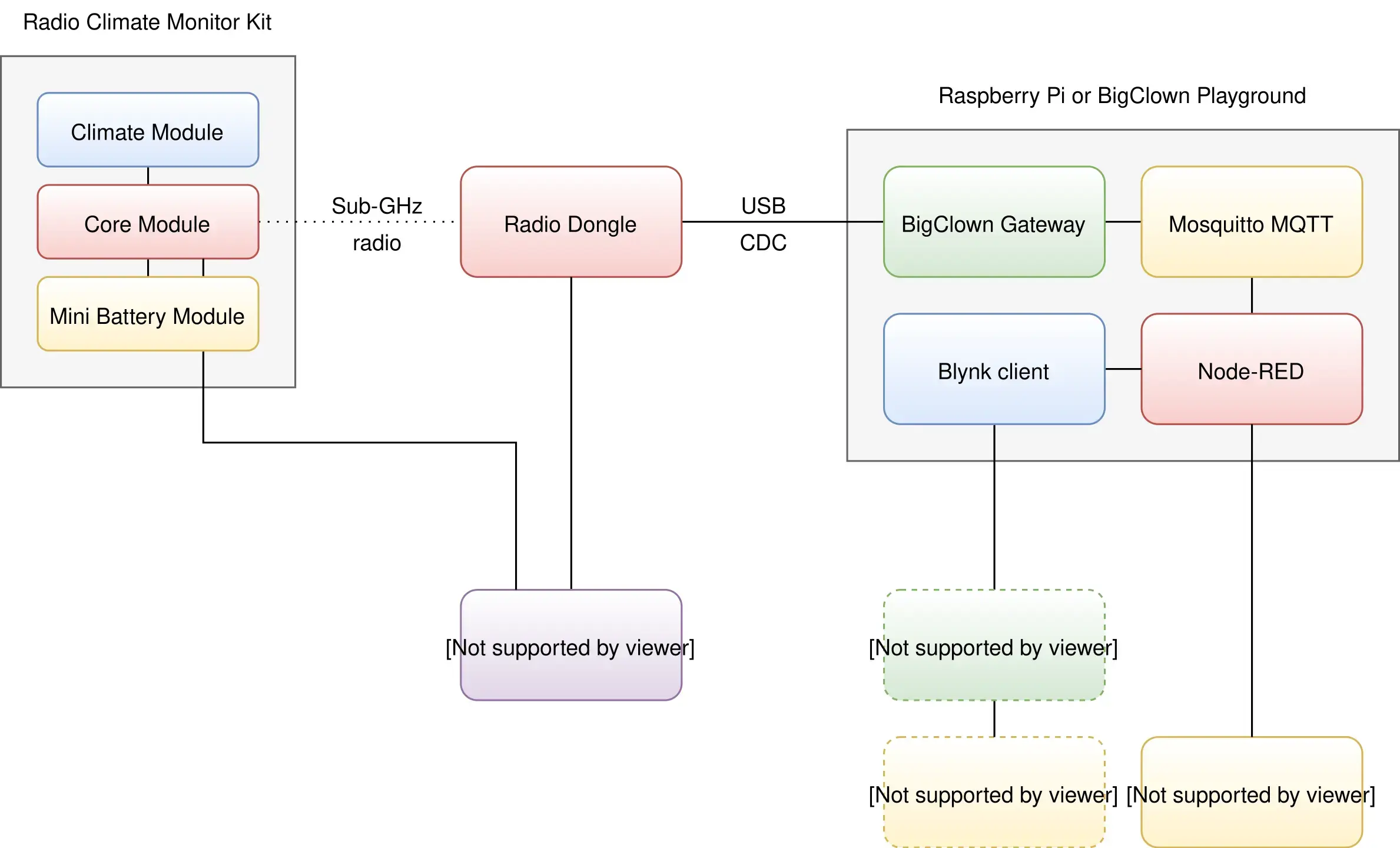
Block Concept
Requirements
-
Either Clime Set, or individual components:
- 1x Climate Module
- 1x Core Module
- 1x Mini Battery Module
- 1x Radio Dongle
-
One of these options:
- HARDWARIO Playground installed (recommended) You can find more information in the Quick Start Guide document.
- Raspberry Pi with the HARDWARIO Raspbian distribution You can find more information in the document Raspberry Pi Installation.
- HARDWARIO Toolchain installed You can find more information in the document Toolchain Setup.
Firmware Upload
In this procedure we will use the HARDWARIO Playground to upload firmware to the Core Module.
Step 1: Connect the Micro USB cable to the Core Module and your computer
Step ****2: Run the HARDWARIO Playground. In the Firmware tab choose and upload the bcf-radio-climate-monitor firmware to the Core Module
Flashing Core Module R1 & R2 For differences of flashing older Core Module 1 and newer Core Module 2 please read Core Module R1 and R2 comparison in the Hardware section
Step 3: Remove the Micro USB cable from the Core Module and your computer
At this point your firmware is successfully uploaded.
Hardware Assembling
See short video with easy step by step demonstration:
Step 1: Start with the Mini Battery Module
Make sure the Mini Battery Module does not have batteries inserted.
Step 2: Plug the Core Module on top of the Mini Battery Module
Step 3: Plug the Climate Module on top of the Core Module
Playground Bootstrap
If you are using the new HARDWARIO Playground, then use the Functions tab instead of using http://localhost:1880/. Also the pairing process is now done in Devices tab. For communication test use the Messages tab.
Step 1: Open Node-RED in your web browser
Step 2: You should see the empty workspace with Flow 1
Step 3: Insert the following snippet in the flow (using Menu >> Import) and click in Flow 1 tab
[{"id":"2fc604fc.3b6abc","type":"inject","z":"dfc861b.b2a02a","name":"List all gateways","topic":"gateway/all/info/get","payload":"","payloadType":"str","repeat":"","crontab":"","once":false,"x":560,"y":460,"wires":[["a2c10833.24d5d8"]]},{"id":"1e4502b8.2f63fd","type":"inject","z":"dfc861b.b2a02a","name":"Start node pairing","topic":"gateway/usb-dongle/pairing-mode/start","payload":"","payloadType":"str","repeat":"","crontab":"","once":false,"x":570,"y":580,"wires":[["795ff5a7.8e266c"]]},{"id":"3d844ce2.932864","type":"inject","z":"dfc861b.b2a02a","name":"Stop node pairing","topic":"gateway/usb-dongle/pairing-mode/stop","payload":"","payloadType":"str","repeat":"","crontab":"","once":false,"x":560,"y":640,"wires":[["5967c452.c838bc"]]},{"id":"f202b253.2705b","type":"inject","z":"dfc861b.b2a02a","name":"List paired nodes","topic":"gateway/usb-dongle/nodes/get","payload":"","payloadType":"str","repeat":"","crontab":"","once":false,"x":560,"y":520,"wires":[["f0aca138.0b2c3"]]},{"id":"349f02fd.890f6e","type":"inject","z":"dfc861b.b2a02a","name":"Unpair all nodes","topic":"gateway/usb-dongle/nodes/purge","payload":"","payloadType":"str","repeat":"","crontab":"","once":false,"x":560,"y":700,"wires":[["2f1c5bb6.53d6f4"]]},{"id":"cf61d75d.4ad8f8","type":"mqtt in","z":"dfc861b.b2a02a","name":"","topic":"#","qos":"2","broker":"67b8de4a.029d3","x":530,"y":400,"wires":[["a5cb0658.f5d658"]]},{"id":"a5cb0658.f5d658","type":"debug","z":"dfc861b.b2a02a","name":"","active":true,"console":"false","complete":"false","x":790,"y":400,"wires":[]},{"id":"a2c10833.24d5d8","type":"mqtt out","z":"dfc861b.b2a02a","name":"","topic":"","qos":"","retain":"","broker":"717f7c18.ba0a24","x":770,"y":460,"wires":[]},{"id":"f0aca138.0b2c3","type":"mqtt out","z":"dfc861b.b2a02a","name":"","topic":"","qos":"","retain":"","broker":"717f7c18.ba0a24","x":770,"y":520,"wires":[]},{"id":"795ff5a7.8e266c","type":"mqtt out","z":"dfc861b.b2a02a","name":"","topic":"","qos":"","retain":"","broker":"717f7c18.ba0a24","x":770,"y":580,"wires":[]},{"id":"5967c452.c838bc","type":"mqtt out","z":"dfc861b.b2a02a","name":"","topic":"","qos":"","retain":"","broker":"717f7c18.ba0a24","x":770,"y":640,"wires":[]},{"id":"2f1c5bb6.53d6f4","type":"mqtt out","z":"dfc861b.b2a02a","name":"","topic":"","qos":"","retain":"","broker":"717f7c18.ba0a24","x":770,"y":700,"wires":[]},{"id":"67b8de4a.029d3","type":"mqtt-broker","z":"","broker":"127.0.0.1","port":"1883","clientid":"","usetls":false,"compatmode":true,"keepalive":"60","cleansession":true,"willTopic":"","willQos":"0","willPayload":"","birthTopic":"","birthQos":"0","birthPayload":""},{"id":"717f7c18.ba0a24","type":"mqtt-broker","z":"","broker":"127.0.0.1","port":"1883","clientid":"","usetls":false,"compatmode":true,"keepalive":"60","cleansession":true,"willTopic":"","willQos":"0","willPayload":"","birthTopic":"","birthQos":"0","birthPayload":""}]
It will look like this:
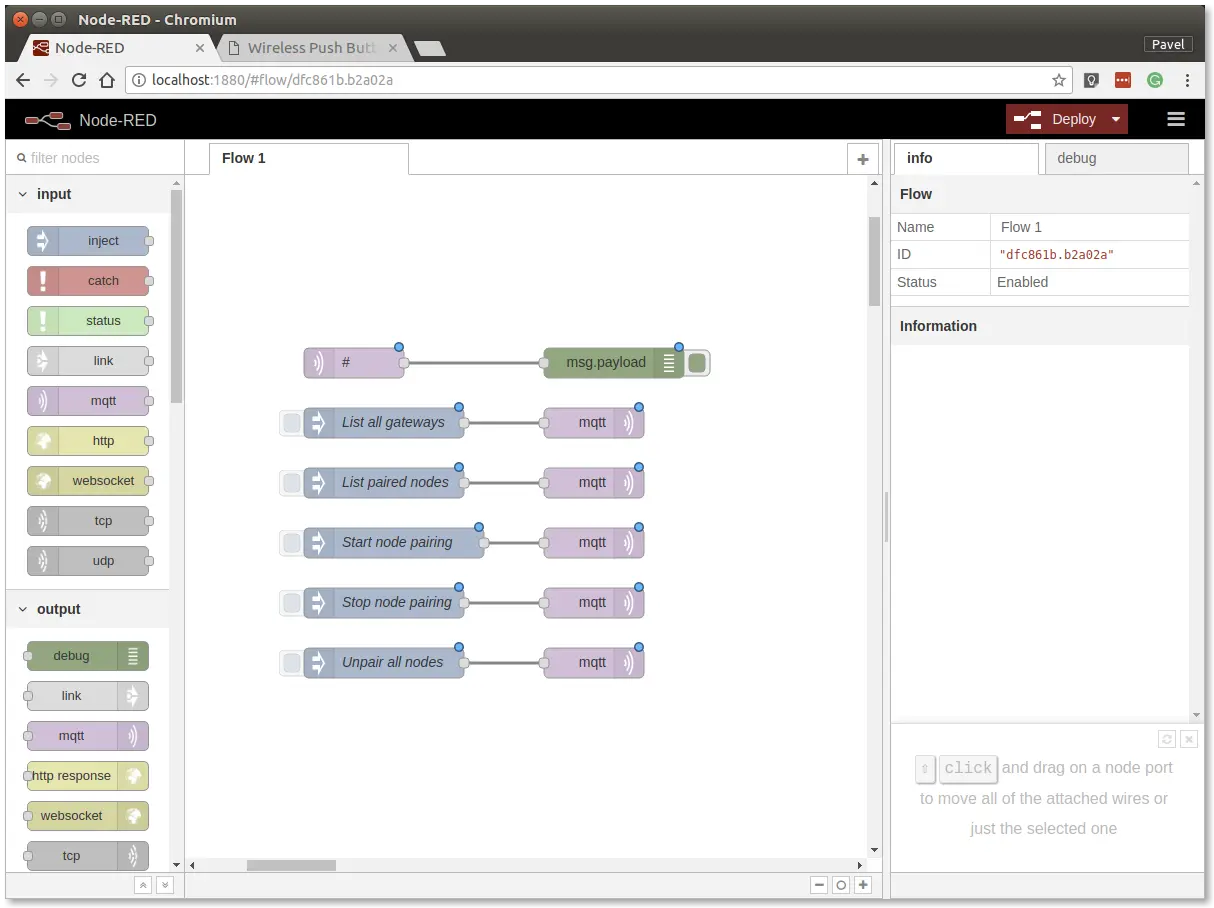
This snippet provides control buttons for gateway/radio commands. These commands are sent over the MQTT protocol.
Step 4: Deploy the flow using the Deploy button in the top-right corner
Step 5: Open the debug tab
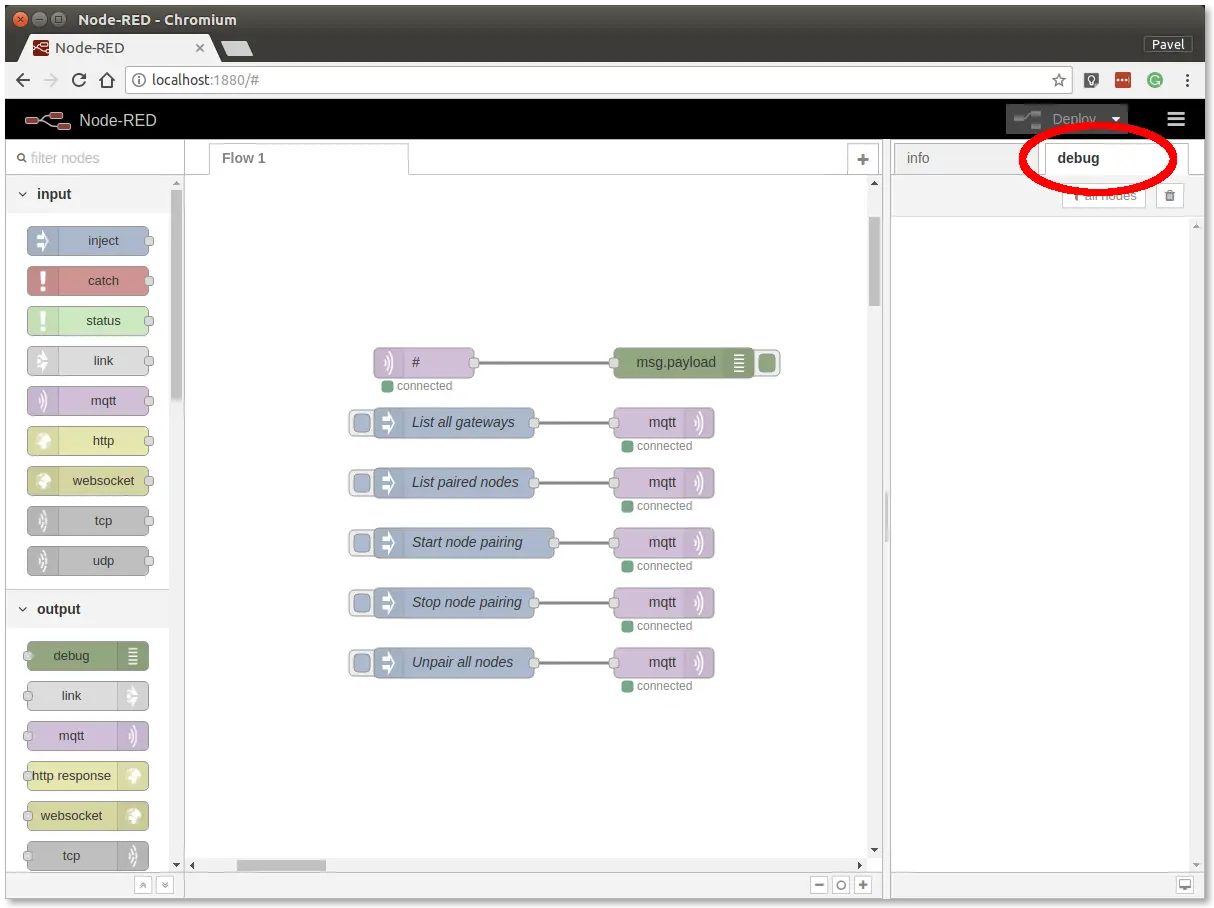
In the debug tab, you will be able to see all the MQTT messages.
Step 6: Click on the List all gateways button. You should see a response like this in the debug tab
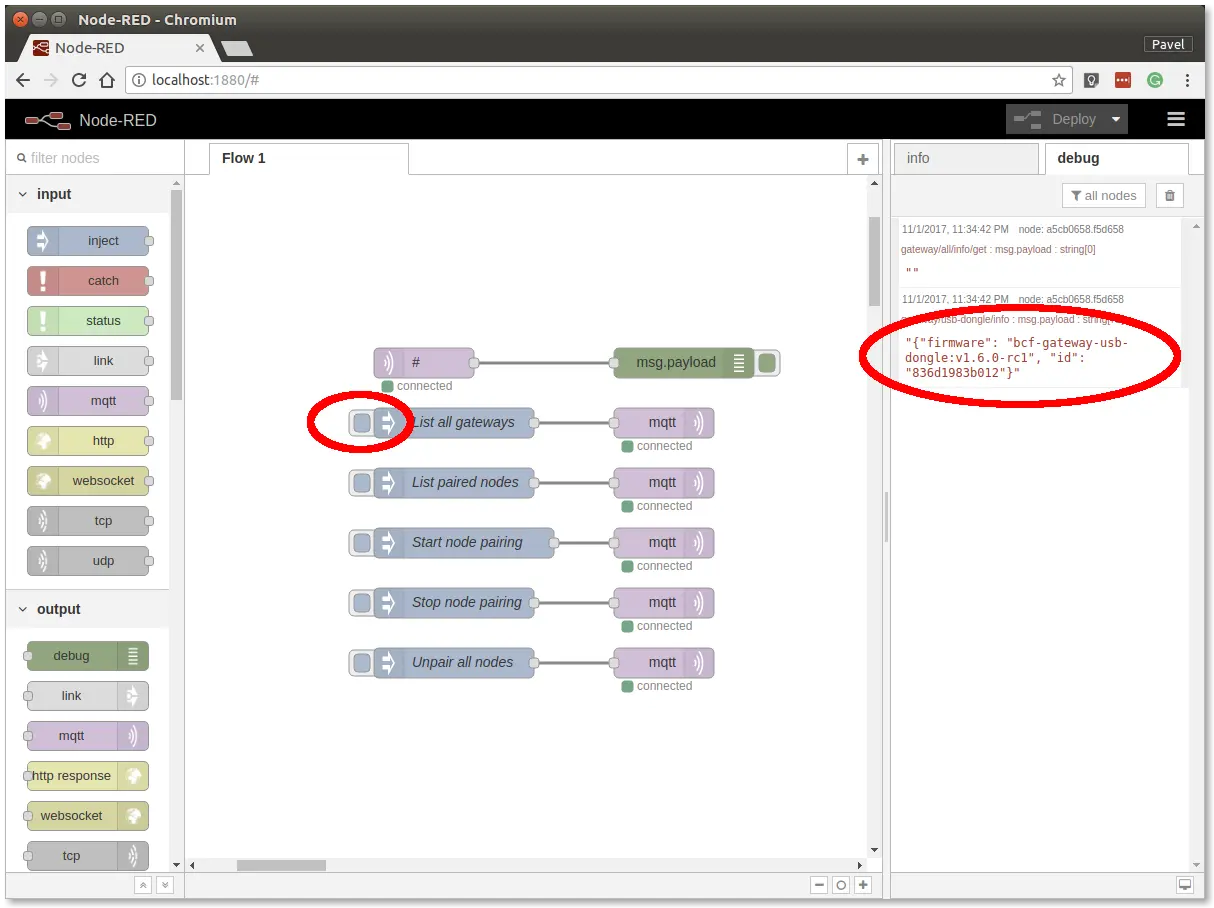
At this point, you've got working Node-RED, MQTT, HARDWARIO Radio Dongleand HARDWARIO Gateway.
Radio Pairing
In this section, we will create a radio link between the Radio Dongle and the Radio Climate Monitor.
Follow these steps in Node-RED:
Step 1: Click on the Start node pairing button
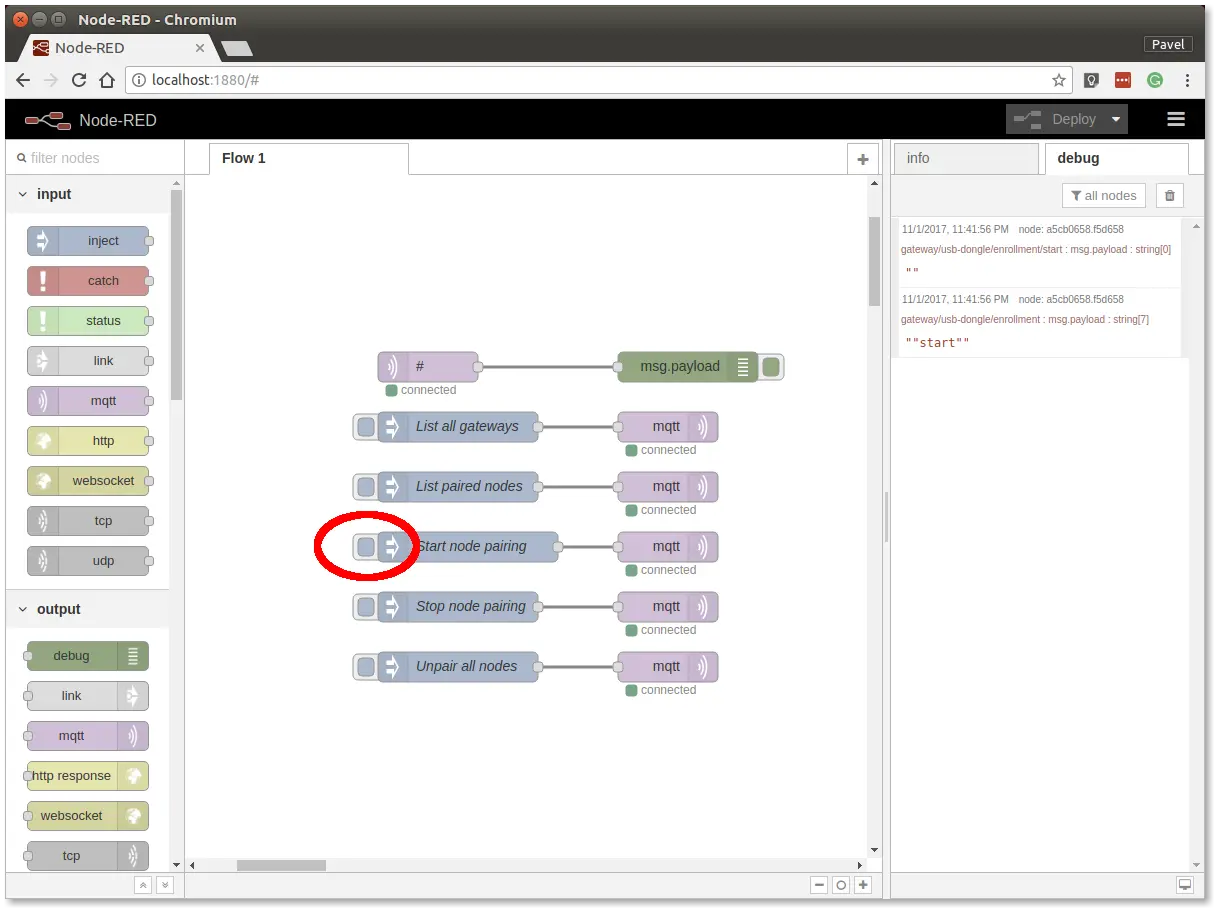
Step 2: Pair Climate Monitor
Insert the batteries into the Radio Climate Monitor to send the pairing request (you should also see the red LED on the Core Module to be on for about 2 seconds).
Step 3: Click on the Stop node pairing button
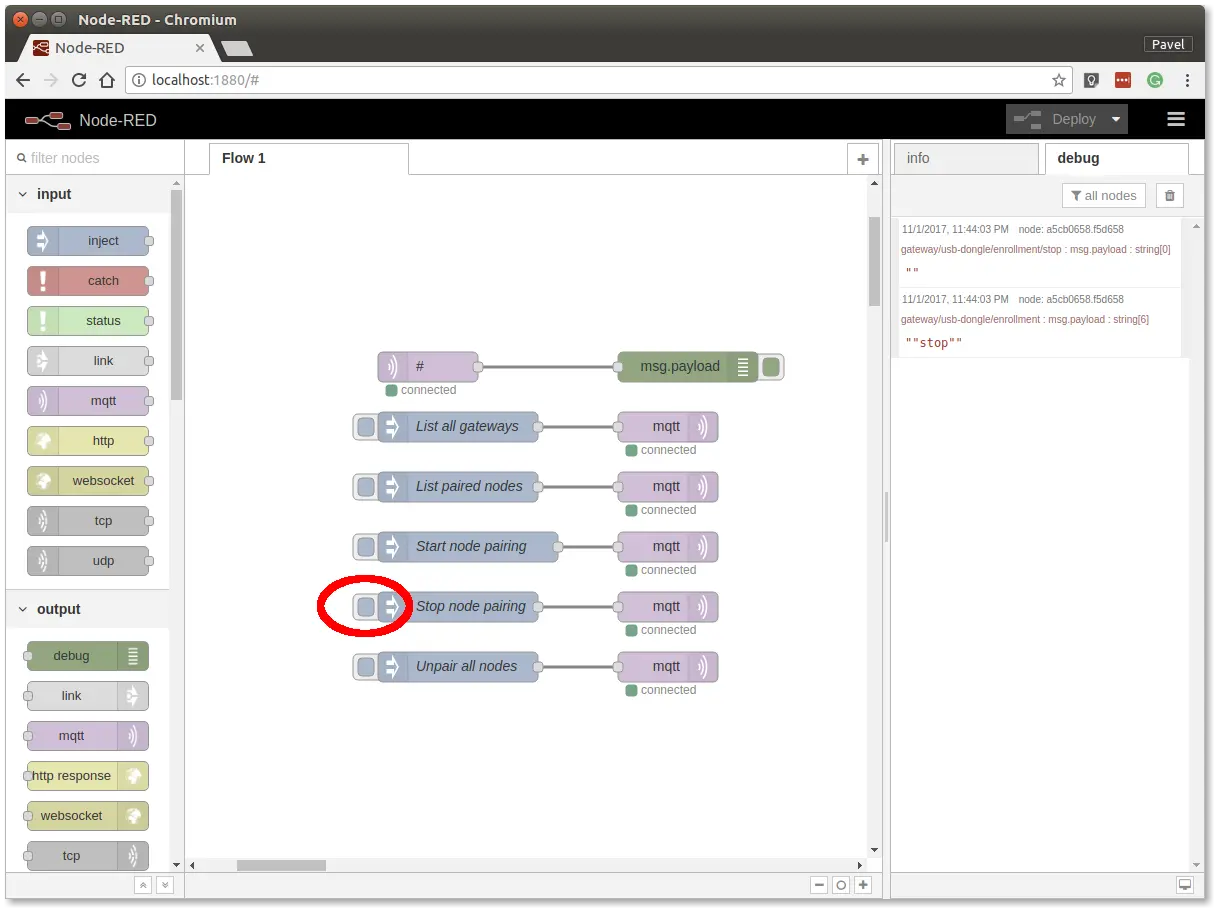
At this point, you've got established a radio link between the node (Radio Climate Monitor) and the gateway (Radio Dongle).
Communication Test
Follow these steps in Node-RED:
Step 1: Switch to debug tab on the right
Step 2: Test connection
Start breathing on the temperature sensor on the Climate Module to invoke a change of temperature and hence trigger a radio transmission.
You should then see similar messages:
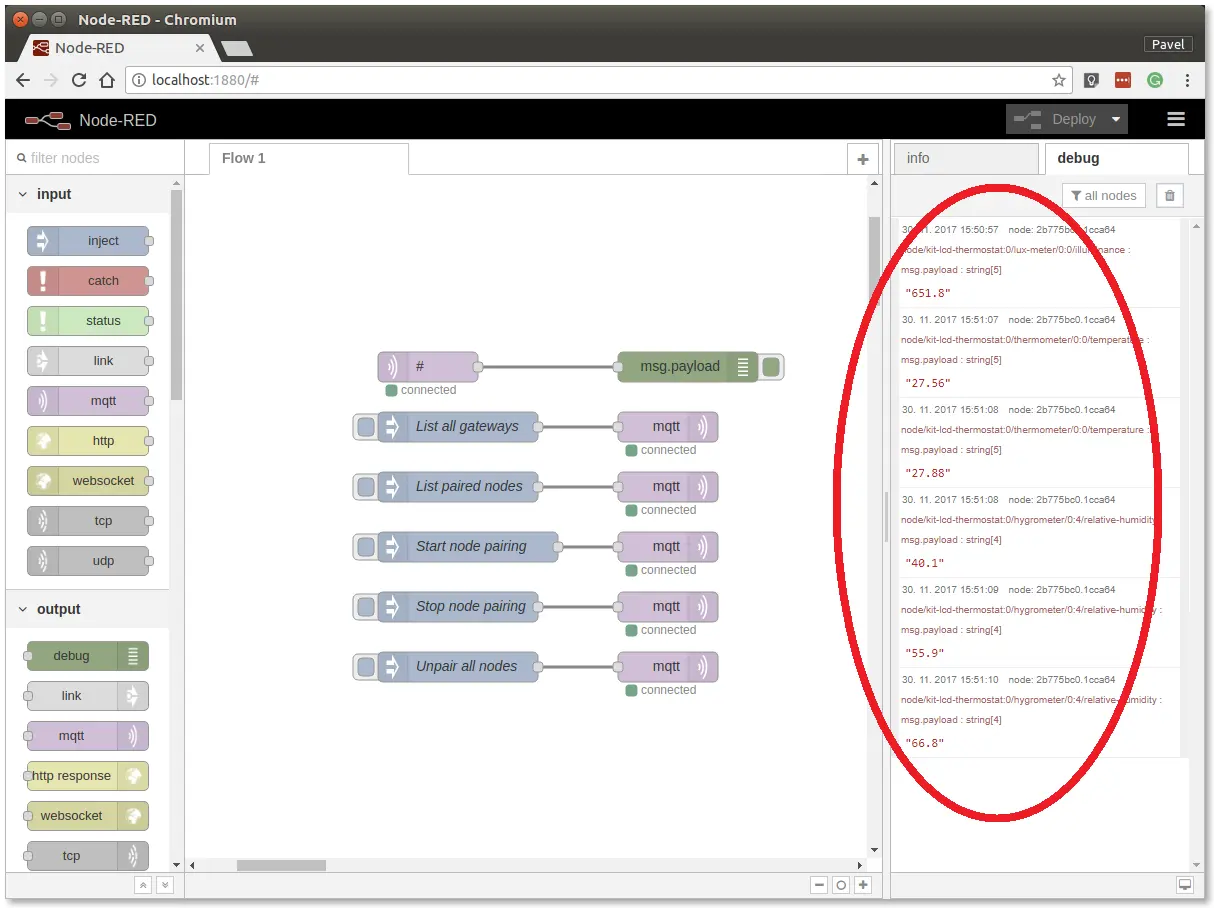
At this point, you've got verified radio communication.
Enclosure
Optionally put the assembly into the appropriate enclosure, if you have one.
You can find more information about the enclosures in the document Enclosures.
Integration with Blynk
Now we have assembled our kit and let's start with some basic integration with Blynk. We will start without describing what Blynk is. If you want get some information about what Blynk is. The best thing you can do is visit their page. In our example we will be showing you how to display graphs from sensor's values in Blynk's mobile application.
Firstly we need to configure our Node-RED app.
Step 1: Blynk nodes
If you are using HARDWARIO raspi version you should be fine, but still check that Blynk nodes are installed. (You can view them on the left side menu in Node-RED). Otherwise you will need to install Node-RED package node-red-contrib-blynk-ws.
Step 2: Add another Flow (you can add them by big plus button next to the flow name). The new flow will have name Flow 2
Step 3: Insert the following snippet in the newly created Flow 2 (using Menu >> Import)
[{"id":"4914605c.76972","type":"mqtt in","z":"28050251.59dc0e","name":"","topic":"node/climate-monitor:0/lux-meter/0:0/illuminance","qos":"2","broker":"58254712.b61068","x":230,"y":520,"wires":[["431157f1.546248"]]},{"id":"dcf5bf8d.a0242","type":"mqtt in","z":"28050251.59dc0e","name":"","topic":"node/climate-monitor:0/thermometer/0:0/temperature","qos":"2","broker":"58254712.b61068","x":240,"y":580,"wires":[["be96b6aa.eed098"]]},{"id":"2ac2eae7.308486","type":"mqtt in","z":"28050251.59dc0e","name":"","topic":"node/climate-monitor:0/hygrometer/0:4/relative-humidity","qos":"2","broker":"58254712.b61068","x":250,"y":640,"wires":[["dbe4b438.be4ef8"]]},{"id":"431157f1.546248","type":"blynk-ws-out-write","z":"28050251.59dc0e","name":"Pin V0 - Write","pin":0,"pinmode":0,"client":"1b003066.8ca2c","x":659,"y":520,"wires":[]},{"id":"be96b6aa.eed098","type":"blynk-ws-out-write","z":"28050251.59dc0e","name":"","pin":"1","pinmode":0,"client":"1b003066.8ca2c","x":659,"y":580,"wires":[]},{"id":"dbe4b438.be4ef8","type":"blynk-ws-out-write","z":"28050251.59dc0e","name":"","pin":"2","pinmode":0,"client":"1b003066.8ca2c","x":659,"y":640,"wires":[]},{"id":"58254712.b61068","type":"mqtt-broker","z":"","broker":"127.0.0.1","port":"1883","clientid":"","usetls":false,"compatmode":true,"keepalive":"60","cleansession":true,"willTopic":"","willQos":"0","willPayload":"","birthTopic":"","birthQos":"0","birthPayload":""},{"id":"1b003066.8ca2c","type":"blynk-ws-client","z":"","name":"","path":"ws://blynk-cloud.com/websockets","key":"","dbg_all":false,"dbg_read":false,"dbg_write":false,"dbg_notify":false,"dbg_mail":false,"dbg_prop":false,"dbg_low":false,"dbg_pins":""}]
It will look like this:
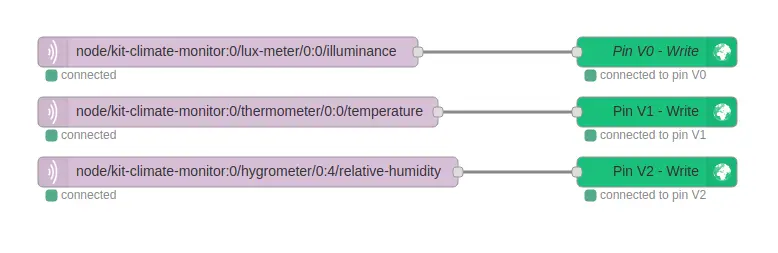
In case you want use it for another sensors just change MQTT topics.
Step 4: Connect
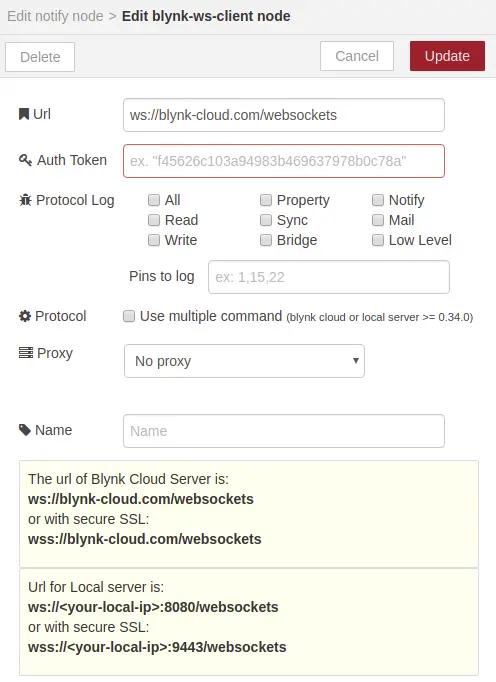
Configure MQTT node to connect it on you broker. It will propably connect on localhost if you are using Raspberry Pi. After that you will need to configure Blynknode. Just fill in URL ws://blynk-cloud.com/websockets. The Auth Token we will configure later after obtaining one from Blynk over e-mail.
Step 5: Now download the Blynk app from App Store or Google Play. Create an account and log-in.
Step 6: After installing, you should create account, login and you should see something like that
Step 7: Now click a button on the top right to scan QR code
Step 8: Now you should scan following QR code to get everything preconfigured
Step 9: You should see something like this
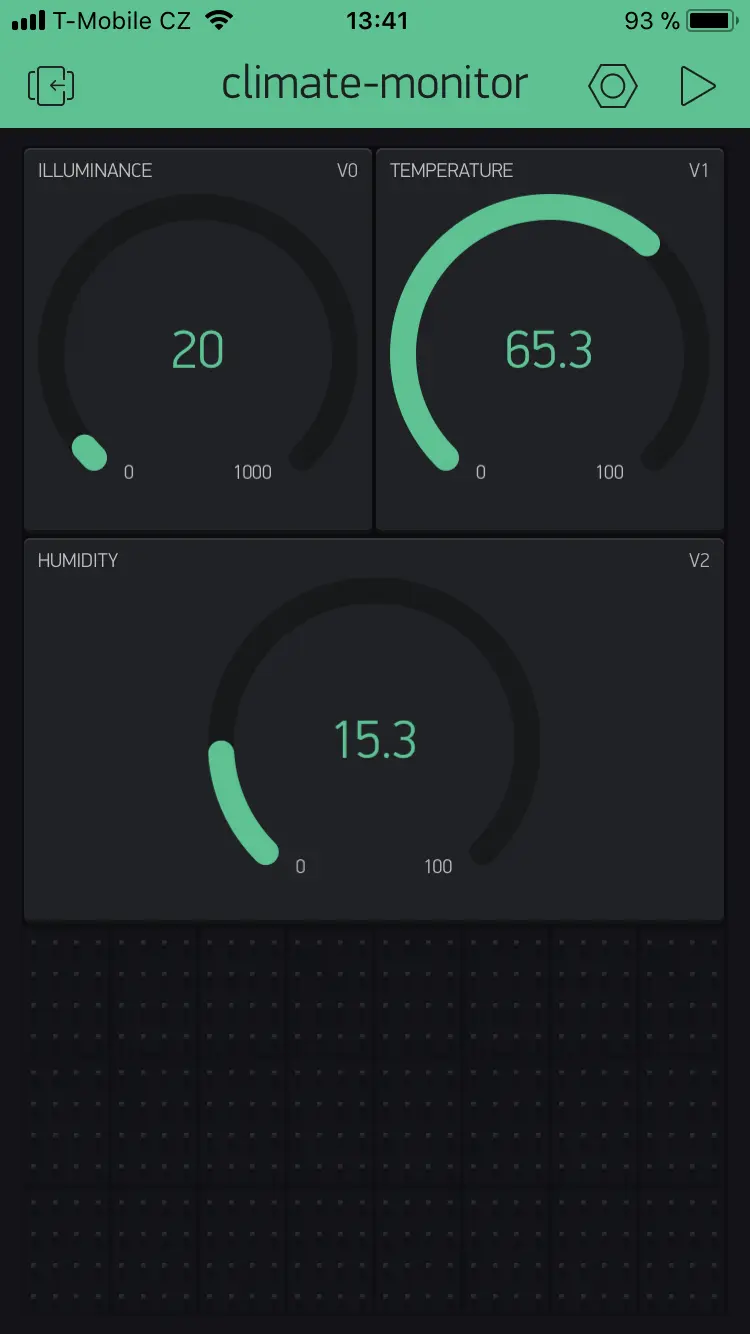
Step 10: Email
Click the settings wheel and you should see settings for your project. We need to get Auth Token which you have to copy to our Node-RED in Blynk node configuration.